Autonomous Ride-Hailing Has Arrived!
Waymo's success in the last year has proven the viability and accpetance of autonomous ride-hailing services. It will transform transportation.
This newsletter explores how technology is changing our lives. Recently, I’ve been discussing generative AI, but in this article, I focus on another major technological shift: the transformation of transportation through autonomous ride-hailing services. This is part of my soon-to-be-published update for Autonomous Vehicles: Opportunities, Strategies, and Disruptions.
Autonomous vehicles will dominate ride-hailing and introduce new transportation options. To illustrate this, I’ll review Waymo's progress as the leader. Waymo’s autonomous vehicles have evolved from a “moonshot” to the leader in autonomous ride-hailing.
If you are interested in generative AI, my recent book has become very popular and is available on Amazon.
Autonomous ride-hailing services (ARS) are here! After years of delays and billions invested, driverless AVs now provide reliable paid trips at a growing rate. Waymo is demonstrating its viability and commercial success. Waymo has surpassed 100 million fully autonomous miles driven on public roads, meaning it was driven without a human behind the wheel, as of mid-2025. Reaching one hundred million miles is a significant milestone. It has completed over 10 million paid rides in its ARS. Currently, its commercial service operates in five major U.S. cities: Phoenix, San Francisco, Los Angeles, Austin, and Atlanta, offering more than 250,000 paid driverless rides weekly. This clearly shows a level of commercial achievement. Waymo has moved beyond proof of concept to operational reality. Its methodical approach to safety, technological sophistication with the Waymo Driver platform, expanding manufacturing capabilities, and accelerating geographic rollout position it as the clear leader in transforming urban mobility through autonomous vehicles.
As proof of market acceptance, Waymo is leading the shift away from traditional ridesharing. In the San Francisco ride-hailing market, Waymo has gained significant market share. According to reports from mid-2025, Waymo had captured approximately 27% of the city’s ride-hailing market after about 20 months of operation. This positions it ahead of Lyft.
The company’s growth from a few pilot cities to a planned network of over 20 U.S. cities, along with international markets, signals a critical turning point. Waymo is shifting from an autonomous vehicle pioneer to laying the groundwork for a new transportation genre, one that aims to make roads safer, mobility more accessible, and urban transit fundamentally changed.
Waymo Background
Waymo has a long history. It began in 2009 as the Google Self-Driving Car Project, an ambitious effort within Google’s X Lab. Initially led by Sebastian Thrun, who had previously won the DARPA Grand Challenge for autonomous vehicles, the project aimed to develop technology that could fundamentally transform transportation and lower traffic accidents.
In 2016, the project was spun off as Waymo LLC, an independent subsidiary of Google’s parent company, Alphabet. This move marked a shift from pure research to commercialization, with John Krafcik appointed as its first CEO. The name “Waymo” was derived from its mission to discover “a new way forward in mobility.”
Throughout its development, Waymo has gone through several vehicle versions. It started with modified Toyota Prius cars, then moved to Lexus SUVs. Later, Waymo began customizing production vehicles, mainly Chrysler Pacifica minivans and Jaguar I-PACE electric SUVs, which are equipped with their own sensor suite and computing platform. Its next-generation vehicle is the ZEEKR RT van, based on the ZEEKR MIX.
Financially, Waymo has received substantial investments. Operating within Alphabet’s Other Bets division, Waymo raised $2.25 billion in its initial external funding round in 2020, followed by an additional $750 million. In 2021, the company secured another $2.5 billion. Although Alphabet rarely discloses specific financial details about Waymo, analysts estimate its valuation ranges between $30 billion and $50 billion at different times, highlighting both the potential and uncertainties in the autonomous vehicle industry.
Commercial Deployment and Aggressive Expansion
ARS is implemented by metropolitan areas, just as Uber launched its ridesharing service. Waymo started cautiously but has now shifted to aggressive growth.
Waymo’s commercial deployment began with Waymo One, its autonomous ride-hailing service launched in Phoenix in 2018. Initially run with safety drivers, the service transitioned to fully driverless vehicles in 2020. A significant milestone took place on October 8, 2020, when Waymo made its fully driverless service available to the public in the Phoenix area, allowing riders to hail vehicles without a human driver behind the wheel.
The company has since expanded systematically to San Francisco (with paid driverless service approved in August 2023 and fully open to the public in June 2024), Los Angeles (public access started in March 2024 and opened to everyone in November 2024), Austin (via Uber partnership in 2025), and Atlanta (launched on the Uber app in June 2025).
In 2024 alone, it provided over 4 million fully autonomous rides and more than 5 million rides in total. Riders have enjoyed over 1 million hours in Waymo vehicles across its operational cities, covering more than 500 square miles of service area.
Aggressive National and International Expansion
Waymo is implementing an aggressive geometric expansion strategy. The company starts in new markets with an initial service area plan, then gradually broadens that area while increasing services and adding more autonomous vehicles. As residents become more comfortable with autonomous services, adoption rates rise and market share grows. At the same time, Waymo enters new metropolitan areas each year and repeats the same expansion process, creating a compounding growth trajectory.
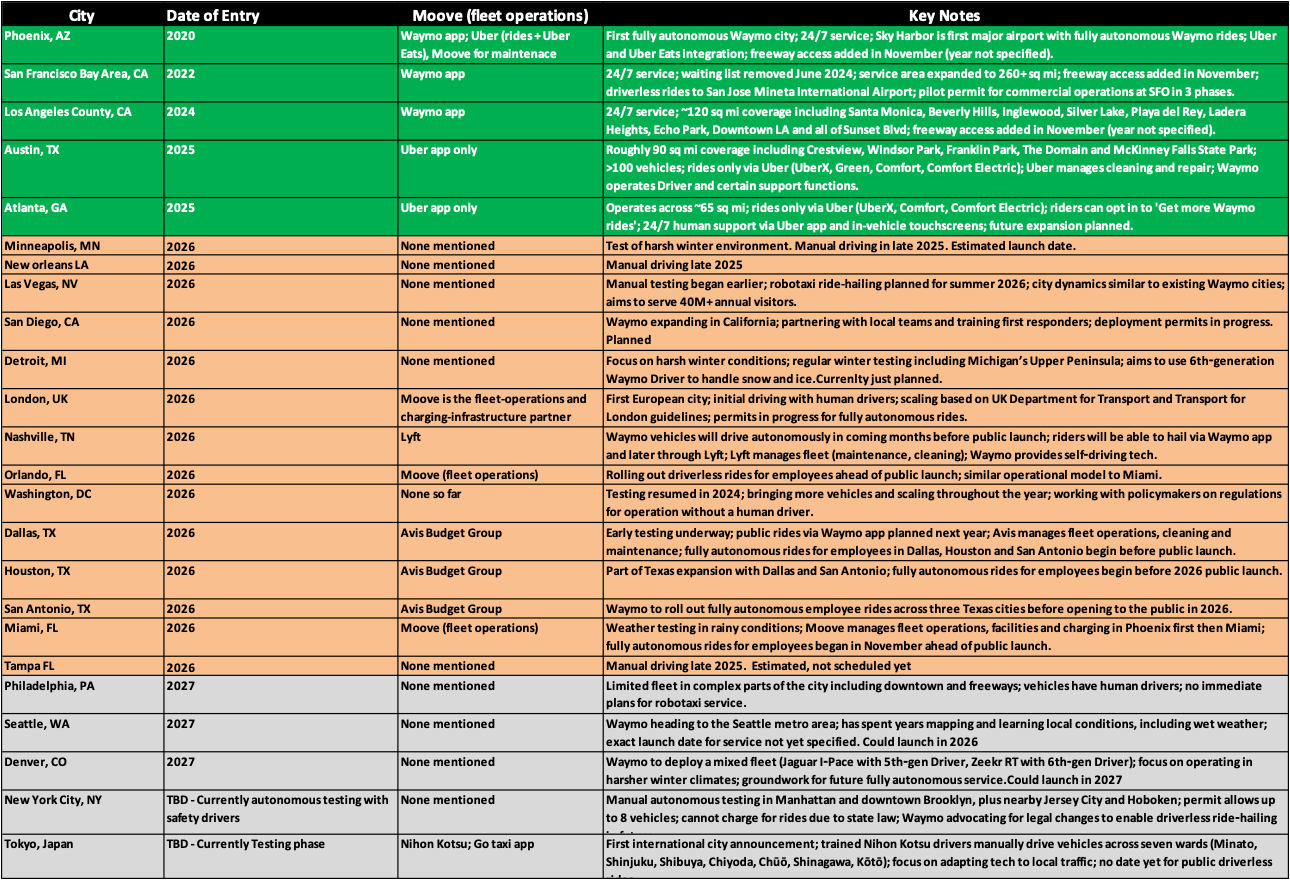
The chart below summarizes Waymo’s expansion plans, dividing the five metropolitan areas it currently serves, 14 more where it has announced expansion plans for 2026, and five additional locations where it has expressed intentions but hasn’t set a target date yet. Two of these announced metropolitan areas are international: London and Tokyo.
Immediate Expansion (2025-2026)
In November 2025, Waymo announced it would begin deploying fully autonomous rides for employees in five new cities—Miami, Dallas, Houston, San Antonio, and Orlando—before launching to the public in 2026. Operations first started in Miami, with the other four cities following in the following weeks. This expansion doubles the number of cities where Waymo operates without a human driver on board.
Beyond these Texas and Florida markets, Waymo has announced launches in several more cities in 2026.
Las Vegas: Waymo plans to launch its ride-hailing service in summer 2026. The company noted that Las Vegas’s driving conditions are similar to those of cities where it already operates, positioning it well to serve the city’s more than 40 million annual visitors.
San Diego: As part of Waymo’s latest major California expansion, the company is working to expand deployment permits, collaborate with local teams, train first responders, and strengthen community relationships ahead of a 2026 launch.
Detroit: This presents a significant technical challenge due to severe winter weather. Waymo has consistently tested in Detroit during winter to improve its capabilities on snow and ice, including in Michigan’s Upper Peninsula. The sixth-generation Waymo Driver is specifically designed to operate autonomously in harsher climates.
Nashville: In partnership with Lyft, Waymo will start autonomous driving in the “coming months” before opening to the public in 2026. Riders will summon vehicles through the Waymo app, with eventual integration into the Lyft app. Lyft will oversee fleet operations, including vehicle maintenance and cleaning, while Waymo manages the self-driving technology.
Denver: Waymo began deploying in the fall of 2025 to prepare for future fully autonomous service. The deployment includes Jaguar I-PACE vehicles with fifth-generation technology and ZEEKR RT vehicles with the sixth-generation Waymo Driver, designed for harsh winter conditions and tested in Michigan, upstate New York, and the Sierra Nevada.
Seattle: Waymo announced it is expanding into the Seattle metropolitan area, citing years of preparation, an understanding of local communities, and the area’s notoriously wet weather.
Washington, D.C.: Waymo plans to begin offering rides through its Waymo app in 2026. The company returned to the nation’s capital in January 2025 to test its autonomous driving technology, bringing more vehicles to the city and working throughout the year to expand its service. Waymo is collaborating closely with policymakers to establish the regulations needed to operate without a human driver in the District.
New York City Challenges
In June 2025, Waymo returned to New York City after initially operating manually there in 2021. The company started driving manually in Manhattan, parts of downtown Brooklyn, and nearby Jersey City and Hoboken. Waymo filed a permit application with the New York City Department of Transportation to operate autonomously with a human behind the wheel, which was approved in late August.
However, current laws in New York State do not allow the fully autonomous ride-hailing service that Waymo offers elsewhere. The company is pushing for changes in state law that would enable vehicles to operate without a human driver, with plans to introduce its fully autonomous service to New York City in the future.
International Expansion
Waymo’s expansion is not just limited to the U.S. It also plans to launch its service into two significant foreign markets:
London: In mid-October 2025, Waymo announced that its vehicles would be heading to London, marking the company’s first location in Europe. Vehicles will initially operate with humans behind the wheel while laying the groundwork for fully autonomous operations. Waymo plans to scale up in line with guidelines from the UK Department for Transport and Transport for London, working closely with local and national leaders to secure the necessary permissions to offer fully autonomous rides in 2026.
Tokyo: In December 2024, Waymo announced Tokyo as its first international location, partnering with Japanese taxi service Nihon Kotsu and taxi app Go. By April 2025, trained Nihon Kotsu drivers started manually operating Waymo vehicles across seven Tokyo wards (Minato, Shinjuku, Shibuya, Chiyoda, Chūō, Shinagawa, and Kōtō) to enable engineers to test and adapt autonomous driving technology to local road features and traffic patterns.
Demonstrated Safety Leadership
Waymo’s autonomous vehicles have proven to be much safer than human drivers. A comprehensive study released in December 2024 by Swiss Re, one of the world’s top reinsurers, clearly demonstrated this. The study examined liability claims arising from collisions over 25.3 million miles driven autonomously by Waymo, using overall auto liability claims data as a proxy for at-fault accidents.
The study compared Waymo’s liability claims to those of human drivers, using Swiss Re’s data from over 500,000 claims and more than 200 billion miles of exposure. The results were striking: the Waymo Driver showed an 88% decrease in property damage claims compared to human-driven vehicles, and an impressive 92% decrease in bodily injury claims. Over 25.3 million miles, the Waymo Driver was involved in only nine property damage claims and two bodily injury claims. Human drivers would be expected to have 78 property-damage and 26 bodily-injury claims for the same distance.
Waymo’s Safety Impact report, which covers 71 million autonomous miles driven through March 2025, found that its Waymo Driver technology had 88% fewer crashes resulting in serious injuries or worse and 78% fewer injury-causing crashes compared with the average human driver over the same distance in its operating cities. The report also documented significantly fewer crashes involving injuries to pedestrians (93% reduction), cyclists (81% reduction), and motorcyclists (86% reduction).
Market Penetration and Consumer Adoption
Traditional ridesharing is Waymo’s initial target market. The service offers an experience similar to Uber and Lyft but provides several unique advantages. Some riders prefer having the vehicle to themselves to avoid potential distractions or the risks linked with a human driver. Additionally, over time, autonomous ride-hailing services are expected to deliver significant cost savings compared to traditional ridesharing.
Early market-share data shows Waymo’s rapid adoption growth. According to Earnest credit card data, Waymo accounted for about 1% of rideshare spending in the San Francisco area within 2 years of launching. Then, after a major service expansion in early 2024 that increased accessibility, adoption surged significantly. By January 2025, Waymo accounted for over 14% of the San Francisco rideshare market’s spending, an impressive milestone indicating real market disruption. By mid-2027, it reached an estimated 27% market share.
Fleet Growth and Manufacturing Scale
In May 2025, Waymo announced a significant infrastructure investment: a 239,000-square-foot factory for autonomous vehicle integration in Mesa, Arizona, built in partnership with Magna. This facility shows Waymo’s dedication to increasing production and marks the company’s shift from experimental tech to large-scale deployment.
At the time of the factory announcement, Waymo operated over 1,500 vehicles across San Francisco, Los Angeles, Phoenix, and Austin. The new facility is designed to add over 2,000 more fully autonomous Jaguar I-PACE vehicles to the fleet. Notably, Waymo indicated it received its final delivery of Jaguars from the manufacturer earlier this year as the company prepares for future vehicle iterations. By August 2025, press reports citing company disclosures estimated Waymo’s U.S. fleet had grown to approximately 2,000 vehicles, with roughly 800 in the Bay Area, 500 in Los Angeles, and 400 in Phoenix.
The Mesa factory’s adaptable design allows for the integration of Waymo’s upcoming sixth-generation self-driving technology into new vehicle platforms. The facility is built to eventually handle tens of thousands of vehicles each year, with an efficient end-of-line process that enables Phoenix vehicles to go into service roughly 30 minutes after leaving the factory.
Next-Generation Vehicles
Waymo is introducing multiple next-generation autonomous vehicle platforms that will define the future of its service. In August 2024, the company unveiled its sixth-generation Driver technology, featuring enhanced sensors designed to help vehicles navigate extreme weather conditions, a critical capability for national expansion into markets with snow, ice, and heavy rain.
The ZEEKR RT Van
By late 2025, Waymo plans to launch the ZEEKR RT van, based on the ZEEKR MIX and specifically designed as an autonomous ride-hailing vehicle for Waymo. This marks a clear shift from retrofitting existing models to creating purpose-built autonomous vehicles. It’s the first mass-produced, purpose-built autonomous ride-hailing vehicle explicitly created for urban autonomous transportation.
The ZEEKR RT van embodies a “rider-first” philosophy, emphasizing passenger comfort, accessibility, and overall experience. The design addresses urban mobility challenges with a low, flat floor and the removal of the B-pillar, creating a seamless, spacious entry and exit path that especially benefits people with mobility impairments.
The interior maximizes passenger space and comfort with adjustable seating for up to five, intuitive infotainment controls, large windows, and a panoramic roof that enhances the driving experience. The overall aesthetic is minimalist and premium, focusing solely on passenger needs rather than driver requirements. Anticipating changing regulations, the design envisions the possible removal of the steering wheel, further optimizing interior space and creating a more open, inviting environment.
The exterior’s boxy shape is a practical choice that maximizes headroom and creates a feeling of spaciousness, paired with a friendly, approachable look designed to build public trust in autonomous vehicles. The vehicle’s excellent maneuverability and tight turning radius make it well-suited for navigating complex urban areas.
At the core of the ZEEKR RT’s autonomous features is a comprehensive sensor set that includes lidar, cameras, and radar to deliver a 360-degree, high-resolution view of the environment. This sensor system, together with Waymo’s sixth-generation autonomous-driving software and hardware, enables accurate perception, navigation, and real-time decision-making.
Although the ZEEKR RT’s cost is not disclosed, the partnership highlights the creation of a budget-friendly platform for broad autonomous ride-hailing use. Waymo might encounter difficulties importing the ZEEKR RT from China due to U.S. government restrictions and potential tariffs on Chinese vehicles. Still, the company believes it has plans to address these challenges. Deliveries are scheduled for the end of 2025.
Hyundai Partnership
In October 2024, Waymo announced a strategic partnership with Hyundai to incorporate its sixth-generation Driver into the all-electric Ioniq 5 SUV. This vehicle will gradually join the Waymo One fleet, with plans to produce a large number of equipped Ioniq 5s over several years to support Waymo One’s expanding service. Testing with these vehicles is set to start by late 2025, with availability to riders in the subsequent years.
Expanding Service Capabilities
Beyond geographic expansion, Waymo is broadening its service capabilities to serve diverse user needs:
Teen Accounts: Launched in July 2025 in Metro Phoenix, this feature allows 14- to 17-year-olds with parental permission and a linked parent or guardian account to ride unaccompanied in Waymo’s driverless cars across the 315-square-mile service area. This marks a necessary demographic expansion and addresses parental concerns about teenage transportation safety. This is an important new service that traditional ridesharing finds challenging to provide.
Airport Service: Access to airports requires special permits and designated drop-off and pick-up points. Phoenix Sky Harbor International Airport (Terminals 3 & 4) provides 24/7 curbside service and remains the most popular Waymo destination in Phoenix, with hundreds of thousands of trips. San José Mineta International Airport introduced curbside service in November 2025. San Francisco International Airport issued Waymo a permit for commercial operations in mid-September 2025, with a phased rollout starting with an onboard safety driver before expanding to full commercial operations.
Freeway Operations: The November 2025 rollout of freeway access in Phoenix, the San Francisco Bay Area, and Los Angeles significantly improved service utility. Riders can now use Waymo vehicles on major highways, including U.S. 101, I-280, and other key corridors, enabling longer trips, more efficient airport connections, and suburban mobility rather than just inner-city transportation. Freeway capability is scheduled to expand to Austin and Atlanta soon.
Competitive Landscape
Other companies are also entering the autonomous ride-hailing market:
Zoox (Amazon) is making significant progress and is preparing to launch its autonomous service for paying customers in Las Vegas and San Francisco. Its autonomous vehicle is bidirectional and custom-designed, similar to Waymo’s new AV.
Motional and Mobileye remain competitors in the autonomous vehicle industry, but haven’t reached the same commercial scale as Waymo.
Aurora plans to expand into autonomous ride-hailing after succeeding in autonomous trucking, with its focus on freeway development potentially aiding future urban deployment.
Chinese Competitors: Companies such as WeRide and Pony AI will be strong contenders in China. However, Chinese AV companies are likely to be barred from the U.S. market, just as American competitors will face restrictions in China, effectively creating separate competitive spaces.
Tesla’s Robotaxi: Despite Elon Musk’s bold claims, significant technical and regulatory challenges remain for Tesla’s camera-only system, which lacks HD maps and geofencing.
Conclusion
Waymo’s rapid progress signals the actual emergence of driverless autonomous ride-hailing as a commercially viable option. After years of research and significant investment, Waymo has surpassed 100 million fully driverless miles on public roads and completed over 10 million paid rides, clearly showing that autonomous ride-hailing is no longer in the experimental stage. Operating in major markets such as Phoenix, San Francisco, Los Angeles, Austin, and Atlanta, Waymo now offers more than 250,000 paid driverless rides each week, demonstrating both technological maturity and strong consumer demand.
The article emphasizes that Waymo has moved beyond pilot programs into scaled, profitable operations, capturing significant market share, most notably reaching about 27% of San Francisco’s ride-hailing market within twenty months. The company’s safety record has far exceeded that of human drivers, backed by independent findings showing substantial reductions in property damage and injury claims. These accomplishments highlight that autonomous vehicles are not just a supplement to traditional ridesharing; they are a fundamentally safer, more efficient transportation model already in commercial use.
Waymo’s aggressive expansion across the U.S. and into global cities further solidifies that the era of autonomous ride-hailing has begun. The company plans to launch in more than 20 cities, including Miami, Dallas, Houston, San Antonio, Orlando, Las Vegas, and San Diego, as well as international markets such as London and Tokyo. With new purpose-built vehicles like the ZEEKR RT and increased manufacturing capacity enabling large-scale fleet production, Waymo is transitioning from a pioneering tech initiative into a nationwide, and soon global, infrastructure for fully driverless mobility. Its trajectory shows that autonomous ride-hailing is no longer a promise for the future; it is an emerging transportation system already reshaping urban mobility today.
The Buttons
If you think someone you know would be interested in the article, you can share it using this button:
If you are interested in generative AI, my recent book has become very popular and is available on Amazon.
If you aren’t a subscriber to my newsletter, you can get your free subscription with this button:
As always, thank you for reading!
Michael